Promise()构造函数
用于构造一个 promise对象。
executor - 执行器函数
Promise()接收一个双参函数,参数为resolve和reject。executor会被立即执行。
当resolve和reject被调用时,promise对象发生状态变化并执行相对应状态的回调。
除此之外,当executor执行的时候发生错误,会立即返回rejected状态的promise。
参数
- resolve()
- reject()
resolve和reject最多只能接受一个参数,传递多个参数时,除第一个后都会被忽略。
const executor = (resolve,reject) => {
const random = Math.random()
random < 0.5 ? resolve(random) : reject(random)
}
const p = new Promise(executor)
promise对象
一个 promise 对象保存了它当前的状态以及返回值。当 promise 状态发生变更时去执行相对应的回调。
状态
- pending
- fulfilled
- rejected
一个promise通过状态的变更来确定它将执行哪一个回调。
下面有一张mdn的图更好的描述了promise的行为
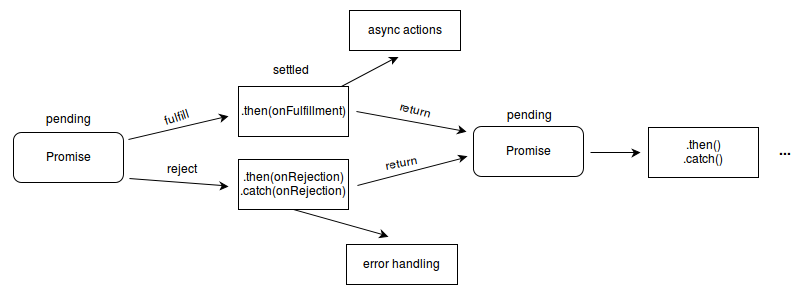
then()
接收两个函数作为参数,可选值,用来注册fulfilled状态和rejected状态的回调。
const onFulfillment = (data) => {
console.log(data)
}
const onRejection = (data) => {
console.log('onRejection',data)
}
p.then(onFulfillment, onRejection)
catch()
catch也可以用来注册rejected状态的回调。
p.then().catch(onRejection)
// 等价
p.then(,onRejection)
finally()
finally注册的回调无论promise处于fulfilled还是rejected都一定会执行。
const onFinally = (data) => {
console.log('onFinally',data)
}
p.finally(onFinally)
// 等价
p.then(onFinally,onFinally)
返回值
promise对象上的api返回值都是promise。
Promise/A+ 标准
An open standard for sound, interoperable JavaScript promises—by implementers, for implementers.
Promise/A+ 标准提供了统一的promise行为。根据标准,则可以实现互相操作的Promise。 原文将放在参考链接里。
统一术语
- promise 是一个拥有符合该标准then方法的对象或函数。
- thenable 是一个拥有then方法的对象或函数。
- value 是promise状态成功时的值,包括 undefined/thenable或者是 promise。
- exception 是一个使用throw抛出的异常值。
- reason 是 promise 处于失败状态时的值。
promise 的状态
- pending
- fulfilled
- rejected
promise 必须处于以上三个状态之一。
处于pending时
- promise 的状态可以变更为 fulfilled 或者 rejected。
处于fulfilled时
- 无法再转变状态。
- 必须有一个 value。
处于rejected时
- 无法再转变状态。
- 必须有一个 reason。
then()
promise必须提供一个then方法来访问最终的value或reason。
接收两个可选参数 onFulfilled 和 onRejected。
参数都必须是函数类型。
onFulfilled存在时
- promise 变为 fulfilled 时, 调用 onFulfilled, 参数为 value 。
- promise的状态不是fulfilled之前不能调用。
- 只能被调用一次。
onFulfilled存在时
- promise 变为 rejected 时, 调用 onFulfilled, 参数为 reason 。
- promise的状态不是 rejected 之前不能调用。
- 只能被调用一次。
onFulfilled 和 onRejected 应该是 异步执行。即应该是 宏任务或者微任务。宏任务可通过 setTimeout 或者 setImmediate(node) ,微任务可通过 MutationObserver 或 process.nextTick(node)。
onFulfilled 和 onRejected 应该被作为函数调用,并且没有this。(严格模式为undefined, 宽松模式应该为全局对象)。
then可以在同一promise上被多次调用
- promise变更为 fulfilled状态时,所有的onFulfilled回调都需要按照then的顺序执行
- promise变更为 rejected状态时,所有的onRejected回调都需要按照then的顺序执行
then必须返回一个promise
promise2 = promise1.then(onFulfilled, onRejected);
- onFulfilled 或 onRejected 返回一个值 x。则运行 Promise Resolution Procedure。
- onFulfilled 或 onRejected 抛出一个异常 e, promise2 必须用 e 作为 reason 被 reject 。
- onFulfilled 不是一个函数并且 promise1 被 resolve 时, promise2必须以同样的值被 resolve 。
- onRejected 不是一个函数并且 promise1 被 reject 时, promise2 必须以同样的值被 reject 。
Promise Resolution Procedure
Promise Resolution Procedure 其实就是一个决定 promise2 和 x 最终行为的函数 ,记为 [[Resolve]](promise, x)。
- 如果promise 和 x 引用同一个对象,用一个TypeError 作为 reason 来拒绝promise。
- 如果x是一个promise,采用它的状态。
- 否则如果 x是一个对象或函数。
- 让then成为x.then
- 如果检索x.then抛出异常 e ,用 e 作为 reason 拒绝 promise。
- 如果then是一个函数, 用x 作为this调用它。 then 方法的参数为两个回调函数。 第一个是 resovlePromise,第二个是rejectPromise:
- 如果resovlePromise用一个 value - y调用,再次允许 [[Resolve]](promise, y)。
- 如果 rejectPromise 用一个 reason - r 调用,用r 拒绝promise。
- 如果 resovlePromise 或 rejectPromise 都被调用, 或者对用一个参数进行多次调用,那么第一个调用优先。以后调用都忽略。
- 如果调用 then 抛出异常。
- 如果 resovlePromise 或 rejectPromise 都被调用, 忽略这个异常。
- 否则 用 e 作为 reason 拒绝 promise。
- 如果 then 不是一个函数 用 x 解决 promise
- 如果 x 不是一个对象或函数, 用 x 解决 promise。
手动实现
通过规范 可以发现 主要分为3个方面。
- 状态。规定了状态的值和状态变化的行为和意义。
- then函数。定义了then函数的行为,是promise的交互接口。
- promise解决程序。 用来决策then函数返回的新promise和then函数接收到的回调被执行后的返回值的行为。
通过查看内置promise对象,可以发现promise并未暴露太多属性。但是很多文章都是通过直接在对象挂载属性,并且未做太多严格的限制,实际可以直接修改自定义实现的很多属性。这里的实现尽量更严格一些。
- 状态只能是pending,fulfilled,rejected之一
- 变为 fulfilled, rejected 后无法再改变
// 状态常量
const PENDING = 'pending'
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled'
const REJECTED = 'rejected'
// 为了不暴露promise的其他信息 用一个全局的WeakMap结构存储所有的 promise 和对应上下文信息
const PromiseCtxsMap = new WeakMap()
// 创建一个promise上下文对象
function createPromiseCtx (resolve, reject) {
return {
resolve,
reject,
// 存储关联 then 函数的上下信息
thenCtxs: []
}
}
// 设置promise上下文对象
function setPromiseCtx(promise, resolve, reject) {
const obj = {
resolve,
reject,
}
if(!PromiseCtxsMap.has(promise)){
PromiseCtxsMap.set(promise, createPromiseCtx())
}
const ctx = PromiseCtxsMap.get(promise)
for(let k of Object.keys(obj)){
if(obj[k]){
ctx[k] = obj[k]
}
}
}
function MyPromise(executor) {
// 判断执行器函数
if (typeof executor !== 'function') {
throw new TypeError(`Promise resolver ${executor} is not a function`)
}
// 拿到promise对象
const promise = this
// 定义存储promise的状态和结果的变量
let PromiseState = PENDING
let PromiseResult = undefined
// 通过 defineProperty 让 状态和结果 暴露出去
Reflect.defineProperty(promise, 'PromiseState', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
get() {
return PromiseState
},
})
Reflect.defineProperty(promise, 'PromiseResult', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
get() {
return PromiseResult
},
})
// 定义 resolve 和 reject
const resolve = function (value) {
// 条件检查
if(PromiseState !== PENDING){
return
}
// 修改状态
PromiseState = FULFILLED
PromiseResult = value
}
const reject = function (reason) {
if(PromiseState !== PENDING){
return
}
PromiseState = REJECTED
PromiseResult = reason
};
// 存储这个promise的 resolve函数和reject
setPromiseCtx(promise, resolve, reject)
// 同步 执行 执行器函数 报错时直接reject这个promise
try {
executor(resolve, reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
return promise
}
关于状态的操作都已经实现了。只有resolve和reject函数可以更改promise的状态。接下来设置then函数的一些行为。
- 再同一个promise上可以多次调用。
- 返回一个promise。
// 创建一个then函数的上下文
function createThenCtx(onFulfilled, onRejected, next) {
return {
// fulfilled状态的回调 非必需
onFulfilled,
// rejected状态的回调 非必需
onRejected,
// 当前then函数返回的新的promise对象
next,
}
}
// 关联then函数的上下文到对应的promise 的 thenCtxs上
function addThenCtx(promise, thenCtx){
const { PromiseState } = promise
const { thenCtxs } = PromiseCtxsMap.get(promise)
}
MyPromise.prototype.then = function(onFulfilled, onRejected){
// 拿到前一个promise
const promise = this
// 生成一个新的pending状态的promise: next
const next = new MyPromise(() => {})
// 处理promise的回调 如果onFulfilled,onRejected不是函数就忽略
if (typeof onFulfilled !== 'function') {
onFulfilled = undefined
}
if (typeof onRejected !== 'function') {
onRejected = undefined
}
// 生成当前then 函数的一些上下文 信息。
const thenCtx = createThenCtx(onFulfilled, onRejected, next)
// 因为同一个promise可以多次调用then,所以把这个promise所有的thenCtx都关联到promise上下文的thenCtxs, 等后面一起做处理
addThenCtx(promise, thenCtx)
// 最后立即返回一个新的promise
return next
}
then函数行为的大致方向已经完成。接下来就是完善细节,处理promise状态变更的执行对应的回调。
// 处理thenCtxs的函数
function flushThenCtxs(promise){
// 提前解构promise的状态和结果,以及 thenCtxs
const { PromiseState, PromiseResult } = promise
const { thenCtxs } = PromiseCtxsMap.get(promise)
while(thenCtxs.length > 0){
// 从数组第一个依次弹出处理
const thenCtx = thenCtxs.shift()
// 拿到当时then函数存入的回调和新的promise
const { onFulfilled, onRejected, next } = thenCtx
const { resolve, reject } = PromiseCtxsMap.get(next)
// 异步处理onFulfilled, onRejected, 然后再根据结果进入promsie 解决程序
setTimeout(() => {
try {
switch (PromiseState){
case FULFILLED:
if(!onFulfilled){
return resolve(PromiseResult)
}
resolvePromise(next, onFulfilled(PromiseResult))
break
case REJECTED:
if(!onRejected){
return reject(PromiseResult)
}
resolvePromise(next, onRejected(PromiseResult))
break
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}, 0)
}
}
// 对 resolve, reject, addThenCtx添加处理thenCtxs的逻辑
function MyPromise(executor) {
// ...other code
const resolve = function (value) {
// ...other code
// 状态变更需要处理thenCtxs
flushThenCtxs(promise)
}
const reject = function (reason) {
// ...other code
// 状态变更需要处理thenCtxs
flushThenCtxs(promise)
}
}
function addThenCtx(promise, thenCtx){
// ...other code
// 如果promise状态已经被敲定了,那么每一次添加addThenCtx都要立即flushThenCtxs
if(PromiseState !== PENDING){
flushThenCtxs(promise)
}
}
最后来实现promsie 解决程序
function resolvePromise(promise, x){
const { resolve, reject } = PromiseCtxsMap.get(promise)
// 同一promise报错
if(promise === x) {
reject(new TypeError(`It's result be the same promise`))
}
// 如果 x 也是 promise,则promise直接关联x的状态
if(x instanceof MyPromise){
// 生成一个新的 thenCtx上下文, 关联到 x 的 thenCtxs
// onFulfilled函数为直接返回值,onRejected为promise的reject
// 行为有点类似于 x.then(y => y, reject), 但是这样会产生一个新的promise
const thenCtx = createThenCtx(y => y, reject, promise)
addThenCtx(x, thenCtx)
} else if(x !== null && (typeof x === 'object' || typeof x === 'function')){
// 如果x是对象或者函数
let then
// 防止检索x.then报错
try {
then = x.then
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
// 不存在then直接用x resolve promise
if(typeof then !== 'function'){
return resolve(x)
}
// 防止多次调用
let called = false
// 立即调用then, 用x作为this,根据规范要求走就行了
try {
then.call(x, function(y){
if(called) return;
called = true
resolvePromise(promise, y)
},function(r){
if(called) return;
called = true
reject(r)
})
} catch (error) {
if(called) return;
reject(error)
}
} else {
resolve(x)
}
}
通过 promises-aplus-tests 验证 Mypromise。
package.json
"scripts": {
"test": "promises-aplus-tests index.js"
},
"devDependencies": {
"promises-aplus-tests": "^2.1.2"
}
在index.js最后添加适配器的代码
var promisesAplusTests = require("promises-aplus-tests");
MyPromise.deferred = function () {
var result = {};
result.promise = new MyPromise(function (resolve, reject) {
result.resolve = resolve;
result.reject = reject;
});
return result;
}
promisesAplusTests(MyPromise, function (err) {
// All done; output is in the console. Or check `err` for number of failures.
});
最后直接执行命令,就可以在控制台看到结果
npm run test
